Potency of Cannabidiol
The potency of Cannabidiol, is the complex interplay between its “bioactivity” or, “binding affinity” to a receptor, and the resulting “signal” that is invoked.
“Binding affinity” refers to the ability of the ligand, to produce a biological response of some magnitude. This response may be an “agonist” (positive response), an “antagonist” (blocks the agonist) or “inverse agonist” (opposite response of the agonist).
The CB2 receptor, Cannabidiol and Bioactivity
BIOACTIVITY IS THE MEASURE OF THE STRENGTH OF THE BOND BETWEEN CBD AND THE CB2 RECEPTOR
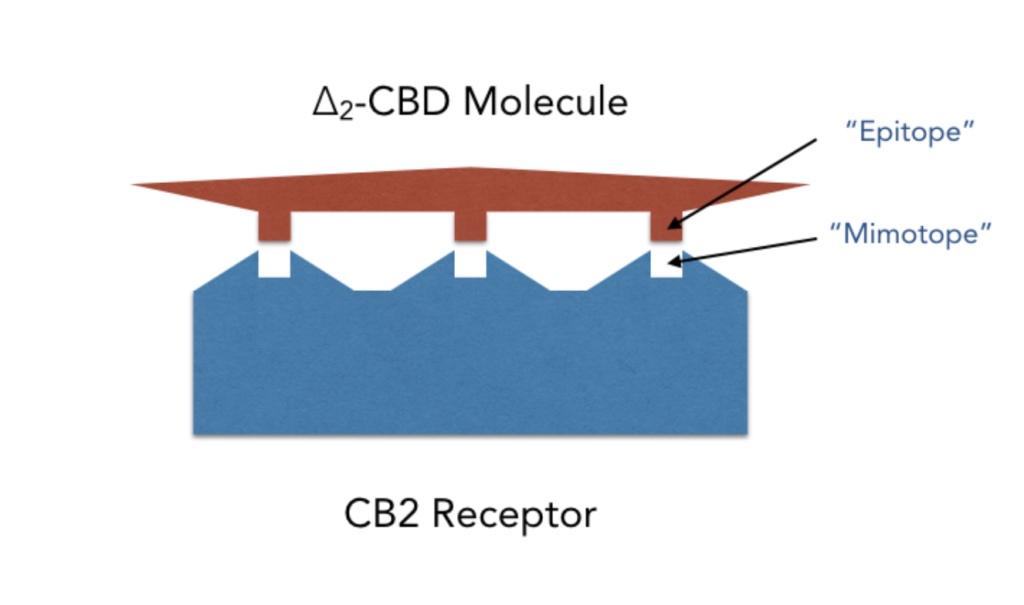
Cannabidiol has a functional response within live tissue. In the case of the bioactivity test, its binding affinity to the CB2 receptor is measured.
The CB2 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor within the endocannabinoid family. This receptor is referred to as the “mimotope”. Cannabidiol has a corresponding site, the “epitope”, which binds to the mimotope. The strength of this bond is called “Bioactivity of CBD”.
